DGA (Dissolved Gas Analysis) is an important tool for checking the healthiness of oil-filled power transformers. Power Transformer is important and expensive equipment in Power Transmission and Distribution systems. Periodic checking or testing of the transformer is done to maintain the healthiness of the transformer.
Transformer oil is used for insulation and cooling of the Transformer. Due to any fault condition or chemical reaction inside the transformer, the oil properties will change and it will generate various gases which are dissolved in the oil.
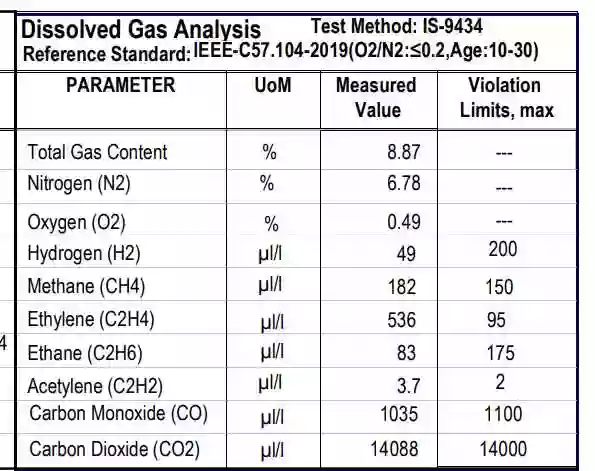
DGA of the oil sample is checked to identify the generated gases inside the oil. Generally, DGA of Transformer oil checks in the testing lab. Portables kits are also available to test DGA at the field.
Transformer oil is a molecule of Hydro carbon, it contains Hydrogen and carbon atoms which are linked by chemical bonds. Due to the decomposition of Transformer Oil and paper insulation of Transformer, it generates the following gases, which are also called DGA gases. The DGA gases are Hydroge(H2), Methene(CH4), Ethane(C2H6), Ethylene(C2H4), Acetylene(C2H2), Carbon Monoxide(CO), Carbon Dioxide(CO2), Oxygen(O2), Nitrogen(N2).
| Gas | Formula | Temperature at which gas forms | Source of Gas |
| Hydrogen | H2 | <150°C for Cold Plasma ionization or corona in oil, >250°C for thermal & delectrical fault | Partial Discharge(PD, Thermal Fault, Power Discharge, sunlight, Rusting |
| Methene | CH4 | 150°C to 300°C | Low and medium temperature thermal faults, Corona partial discharge |
| Ethane | C2H6 | 200°C to 400°C | Low and medium temperature thermal fault |
| Ethylene | C2H4 | 300°C to 700°C | High Temperature thermal fault |
| Acetylene | C2H2 | >700°C | High energy discharge or Arc, Very hot spot |
| Carbon Monoxide | CO | 105°C to 300°C | Thermal fault involving cellulose (paper, pressboard, Wood blocks) slowly from oil oxidation |
| Carbon Dioxide | CO2 | 105°C to 300°C | Thermal fault involving cellulose (paper, pressboard, Wood blocks) slowly from oil oxidation Normal aging |
| Oxygen | O2 | Vacuum in oil or drop in oil temperature | Leakage, Expose of oil to atmosphere |
| Nitrogen | N2 | Vacuum in oil or drop in oil temperature | Leakage, Expose of oil to atmosphere |